Comparison with Latvian SYSTEM
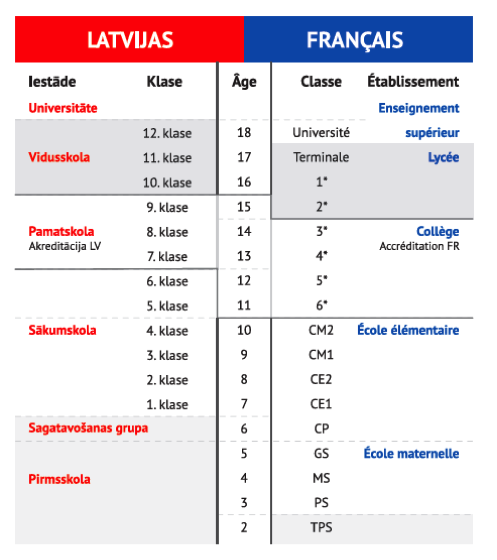
Conformity of Education with the Level and Type of General Education of the Republic of Latvia. Please see the enclosed document.
Samples of education documents:
Primary school certificate and transcript of records (BREVET)
Certificate of Secondary Education and transcript of records (BACCALAUREAT)
Teaching cycles
School since pre-elementary school is divided into 4 cycles of 3 years each that give students more time to learn. Organization in teaching cycles allows learning to be more progressive and takes into account students needs to help them acquire skills.
Pre-elementary school is a cycle on its own
- Cycle 1, first learning cycle, corresponds to the first three years of pre-elementary school respectively named petite section, moyenne section and grande section (small section, middle section and big section);
- Cycle 2, fundamental learning cycle, corresponds to the first three years of elementary school respectively named cours préparatoire, cours élémentaire première année and cours élémentaire deuxième année (preparatory class, elementary class first year, elementary class second year);
- Cycle 3, strengthening cycle, corresponds to the last 2 years of elementary school after the fundamental learning cycle and to the first year of middle school respectively named cours moyen première année, cours moyen deuxième année and classe de sixième (middle class first year, middle class second year and sixth grade). This cycle is both on elementary school and middle school. It aims to support a better pedagogical continuity between school and middle school.
- Cycle 4, deepening cycle, corresponds to fifth, fourth and third grades. During this cycle, students increase their knowledge and skills in all the topics while preparing the future of their education and active participation to society.
- high school.
Common core of knowledge, skills and culture
Mastering at a satisfactory level the common core of knowledge, skills and culture guarantees the requested knowledge to pursue education. This level cannot be limited, each student could aim for a great command.
An assessment is made at least at the end of each cycle, based on the knowledge and skills evaluation, one of those skills being the ability to use resources (knowledge, skills, behaviours) to perform a task or face a complicated or new situation. Develop its skills goes beyond acquiring knowledge while building upon them.
Mastering the common core of knowledge, skills and culture is assessed for each of the following topics:
- languages to think and communicate
- methods and tools to learn
- person and citizen training
- natural and technical systems
- world representation and human activity
The first topic, languages to think and communicate, should itself be assessed separately for the following four goals:
- understand, explain oneself by using French at oral and in writing
- understand, explain oneself by using a foreign language
- understand, explain oneself by using mathematics, sciences and computer science
- understand, explain oneself by using arts and body language
